 |
Athleticsis an exclusive collection of sporting events that involve competitive running, jumping, throwing, and walking. The most common types of athletics competitions are track and field, road running, cross country running, and race walking. The simplicity of the competitions, and the lack of a need for expensive equipment, makes athletics one of the most commonly competed sports in the world. |
History of Athletics
Antiquity and Middle Ages
A copy of the Ancient Greek statue Discobolus, portraying a discus thrower Athletic contests in running, walking, jumping, and throwing are among the oldest of all sports and their roots are prehistoric.[ Athletics events were depicted in the Ancient Egyptian tombs in Saqqara, with illustrations of running at the Heb Sed festival and high jumping appearing in tombs from as early as of 2250 BC. The Tailteann Games were an ancient Celtic festival in Ireland, founded around 1800 BC, and the thirty-day meeting included running and stone-throwing among its sporting events. The original and only event at the first Olympics in 776 BC was a stadium-length running event known as the stadion. This later expanded to include throwing and jumping events within the ancient pentathlon. Athletics competitions also took place at other Panhellenic Games, which were founded later around 500 BC. The Cotswold Olimpick Games, a sports festival which emerged in 17th century England, also featured athletics in the form of sledgehammer throwing contests.Annually, from 1796 to 1798, L'Olympiade de la République was held in revolutionary France, and is an early forerunner to the modern summer Olympic Games. The premier event of this competition was a running event, but various ancient Greek disciplines were also on display. The 1796 Olympiade marks the introduction of the metric system into sport.
Modern era
The Royal Military College, Sandhurst has claimed to be the first to adopt this in 1812 and 1825, but without any supporting evidence. The earliest recorded meeting was organised at Shropshire in 1840 by the Royal Shrewsbury School Hunt. There are details of the meeting in a series of letters written 60 years later by C.T. Robinson, who was a pupil there from 1838 to 1841. The Royal Military Academy at Woolwich held an organised competition in 1849, but the first regular series of meetings was held by Exeter College, Oxford from 1850.

The 100 metres sprint at the 1896 Summer Olympics. The first modern-style indoor athletics meetings were recorded shortly after in the 1860s, including a meet at Ashburnham Hall in London which featured four running events and a triple jump competition. The Amateur Athletic Association (AAA) was established in England in 1880 as the first national body for the sport of athletics and began holding its own annual athletics competition – the AAA Championships. The United States also began holding an annual national competition – the USA Outdoor Track and Field Championships – first held in 1876 by the New York Athletic Club. Athletics became codified and standardised via the English AAA and other general sports organisations in the late 19th century, such as the Amateur Athletic Union (founded in the US in 1888) and the Union des sociétés françaises de sports athlétiques (founded in France in 1889). An athletics competition was included in the first modern Olympic Games in 1896 and it has been as one of the foremost competitions at the quadrennial multi-sport event ever since. Originally for men only, the 1928 Olympics saw the introduction of women's events in the athletics programme. Athletics is part of the Paralympic Games since the inaugural Games in 1960. Athletics has a very high profile during major championships, especially the Olympics, but otherwise is less popular. An international governing body, the International Amateur Athletics Federation (IAAF), was founded in 1912; it adopted its current name, the International Association of Athletics Federations, in 2001. The IAAF established separate outdoor World Championships in 1983. In modern times, athletes can receive money for racing, putting an end to the so-called "amateurism" that existed beforeThe Comité International Sports des Sourds had been formed by 1922, to govern international deaf sports, including athletics. The first organized international competitions for athletes with a physical disability (not deaf) began in 1952, when the first international Stoke Mandeville Games were organized for World War II veterans. This only included athletes in a wheelchair. The first Paralympic Games were held in 1960. Competitions would over time be expanded to include mainly athletes with amputations, cerebral palsy and visual impairment, in addition to wheelchair events.
Member Countries of International Associations of Athletics Federation
Since its foundation in 1912, the international governing body for athletics has been the International Association of Athletics Federations (IAAF). It was initially known as the International Amateur Athletics Federation but changed later its name to reflect that the sport had moved away from amateurism towards professionalism in the late 1970s. The IAAF has 213 member nations and territories, which are divided into six continental areas (or area associations. The six association areas are for Asia, Africa, Europe, Oceania, North America and South America. The sports within athletics do not have their own independent governing bodies at either international or continental level and, instead, all fall under the athletics authorities.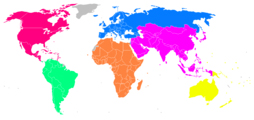
Map of the six continental federations of the IAAF •AAA – Asian Athletics Association •CAA – Confederation of African Athletics •CONSUDATLE – South American Athletics Confederation •NACACAA – North America, Central America and Caribbean Athletic Association •EAA – European Athletics Association •OAA – Oceania Athletics Association National level athletics organizations are responsible for the regulation of the sport within their respective countries and most major competitions have some form of permit or approval from their national body.
Main Competitions of Athletics
International championships
Olympic Games 
The athletics competition underway at the main stadium of the 2008 Summer Olympics.
The modern Summer Olympics was the first event at which a global athletics competition took place. All the four major sports within athletics have featured in the Olympic athletics programme since its inception in 1896, although cross country has since been dropped. The Olympic competition is the most prestigious athletics contest and, in addition to this, many athletics events are also among the most prominent competitions at the Summer Olympics as a whole. A total of 47 athletics events are held at the Olympics, 24 for men and 23 for women. The events within the men's and women's programmes are either identical or have a similar equivalent, with the sole exception being that men contest the 50 km race walk.
Paralympic Games
The Summer Paralympics include athletes with a physical disability. Track and field, and road events have featured in the Paralympic athletics programme since its inception in 1960. The Paralympic competition is the most prestigious athletics contest where athletes with a physical disability compete. Athletics at the Paralympic Games also include wheelchair racing where athletes compete in lightweight racing chairs. Athletes with a visual impairment compete with a sighted guide. At the 2012 Summer Paralympics in London, for the first time at an international athletics event, the guides will receive medals,such as the pilots in cycling, and the guides at the Paralympic Winter Games have done for a while.World Championships
The IAAF World Championships in Athletics is the primary global athletics championships held by IAAF. The biennial competition was first held in 1983 and now features an event program which is identical to the Olympics. Thus, road running, race walking and track and field are the sports which feature at the competition. Cross country running has its own discrete global championships – the IAAF World Cross Country Championships – which has been held annually since 1973. The IAAF World Indoor Championships in Athletics is a biennial athletics championships which features solely indoor track and field events. The foremost separate road running event is the annual IAAF World Half Marathon Championships (formerly World Road Running Championships). While not having official world championship status, the biennial IAAF World Race Walking Cup fulfils a similar role for the sport of race walking. Outdoor track and field is the only sport in athletics that does not have a its own distinct global championship which is separate from other types of athletics, although the IAAF Continental Cup (a quadrennial competition between continental teams) is composed entirely of outdoor track and field events. Other world championships include the IAAF World Junior and World Youth Championships in Athletics, which are for athletes under-19 and under-17, respectively. World Masters Athletics conducts the World Masters Athletics Championships for athletes in 5 year age divisions over the age of 35. The now defunct IAAF World Road Relay Championships served as the global event for ekiden marathon relay races. Elite athletes with a physical disability compete at the IPC Athletics World Championships.Commonwealth Games
Athletics is one of the sports at the quadrennial Commonwealth Games competition. It has been a Commonwealth Games sport since the inaugural edition of the event's precursor, the 1930 British Empire Games. It is a core sport and must be included in the sporting program of each edition of the Games.Universiade
Athletics is one of the sports at the biennial summer Universiade competition. It has been one of the event's competed sports since the inaugural edition. Top
All-Athletics World Rankings - 10.01.2012 (03.01.2012)
Pl. Athlete Birth Nat. Score (Pr.Sc.) Events. (1.) Usain BOLT 86 JAM 1458 (1458) 100m,200m. (2.) Yohan BLAKE 89 JAM 1451 (1451) 100m,200m. (3.) Walter DIX 86 USA 1432 (1432) 100m,200m. (4.) David RUDISHA 88 KEN 1415 (1415) 800m. (5.) Mo FARAH 83 GBR 1413 (1413) 1000m,500m. (5.) Brimin Kiprop 85 KEN 1413 (1413) 3000mSC. (7.) Ezekiel KEMBOI 82 KEN 1412 (1412) 3000mSC. (8.) Jason RICHARDSON 86 USA 1408 (1408) 110mH. (9.) Dayron ROBLES 86 CUB 1404 (1404) 110mH. (10.) Dylan ARMSTRONG 81 CAN 1402 (1402) Shot Put.Top
Top World Athletics
 |
 |
 |
|||
 |
 |